In contrast, the “non-traditional” one is the variable income statement. It is a financial computation of profit that separates variable costs from fixed costs. Contribution margin income statements use variable costing where fixed production costs are included in overhead costs. The cost of goods sold only includes the variable expenses directly tied to production without the fixed cost because it does not affect the sales volume. It offers a breakdown of revenues, expenses, and profits, allowing analysts to gauge the company’s profitability, operational efficiency, and cost management.
Final Thoughts on Traditional (Absorption Costing) Income Statement
Because the job cost sheet definition involves the use of cost allocations within the cost of goods sold block of information, it can be difficult to determine which costs vary with changes in sales. Investors need to know what’s on an income statement so that they can tell if the company’s stock is worth buying. Company executives turn to these financial reports to help them identify ways to improve the company so it can grow competitively. And lenders or creditors may want to see income statement information before making decisions on financing.
Gross profit
Losses include money lost through activities outside of transactions for your primary goods or services. Revenue is all income generated by the sale of the business’ primary goods or services. Revenue may also be referred to as the “top line,” because it is the first line on the income statement.
Types of Financial Statements: A Complete Guide
Then, we’ll dive into how to figure out the operating income, which tells us how much money the company made from its main business. Lastly, we’ll look at calculating the cost of goods sold, an important part of understanding how much it costs to make the products we sell. Each part helps us see the big picture of a company’s financial health. A single-step income statement is a simplified approach to viewing your net profit or loss.
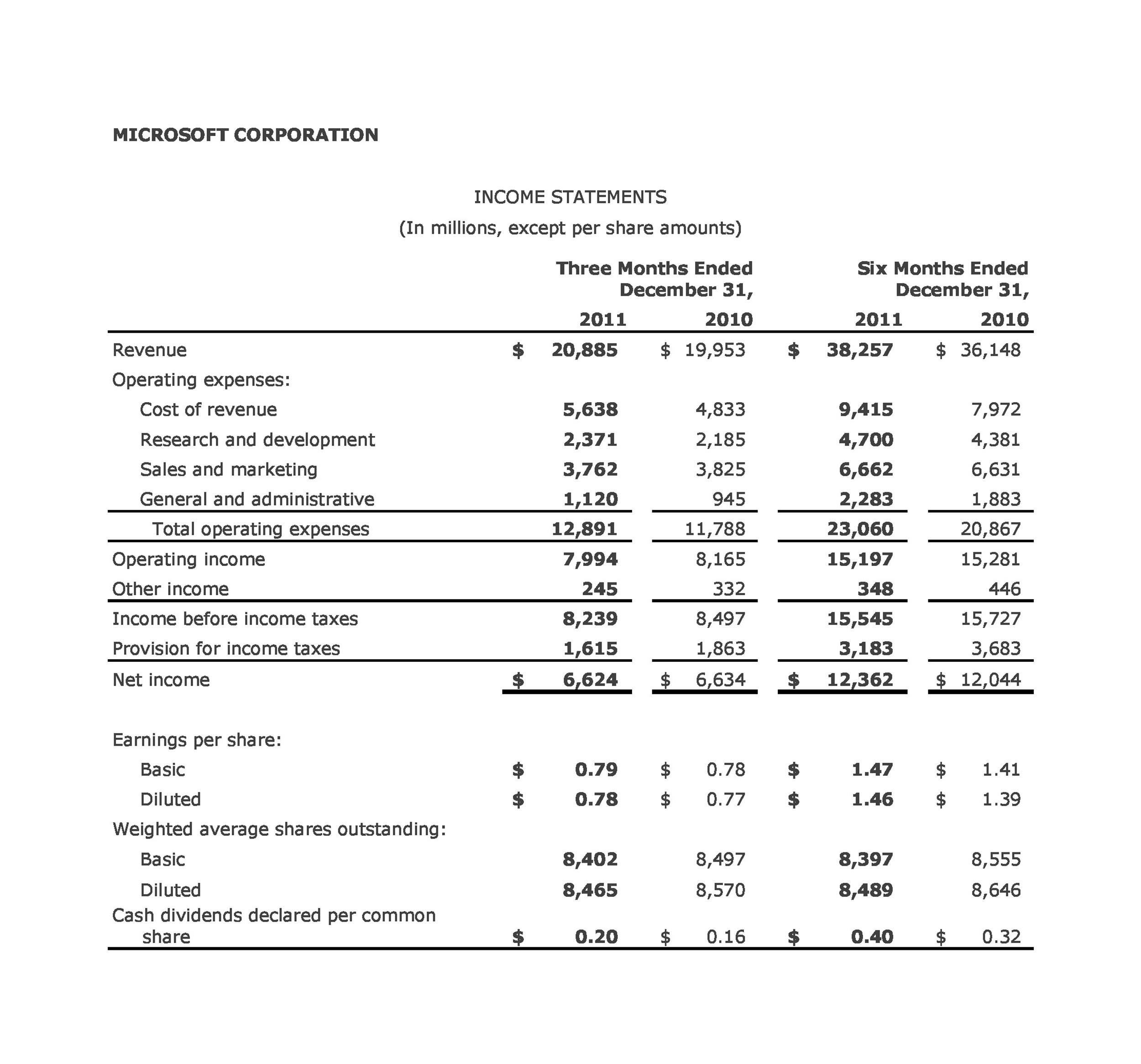
The traditional income statements use absorption costing/ full costing that considers both variable and fixed expenses in the computation. It includes the fluctuating production costs and fixed manufacturing costs in calculating the cost of goods sold like insurance, salaries of workers, and other selling and administrative costs. A traditional income statement provides information on a company’s sales or revenue, cost of goods sold, gross profit, operating expenses, operating income, and net income or loss. In this section, we’re going to learn how to put together a traditional income statement, a key document that shows if a company is making money.
- The financial statements tell the clearest story about a company’s health, spelling out basic events like income, expenses, cash flow, and equity.
- It provides valuable insights into various aspects of a business, including its overall profitability and earnings per share.
- Following operating expenses are other forms of income, known as income from continuing operations.
- If the company has no gains because its costs are greater than its revenue, than it is suffering losses.
Calculate the cost of goods sold for the traditional income statement
A balance report details your end balance for each account that will be listed on the income statement and provides all of the end balances required to create your income statement. You can also look at QuickBooks Online subscription levels and see a comparison of QuickBooks vs. Xero accounting software. Preparing financial statements can seem intimidating, but it doesn’t have to be an overwhelming process. We’ve broken down the steps for preparing an income statement, as well as some helpful tips. Net income—or loss—is what is left over after all revenues and expenses have been accounted for.
Operating expenses are the expenses the company incurs through its normal day-to-day operations. It is also referred to as the cost of sales if the company is offering services. Kristin is a Certified Public Accountant with 15 years of experience working with small business owners in all aspects of business building. In 2006, she obtained her MS in Accounting and Taxation and was diagnosed with Hodgkin’s Lymphoma two months later.
A quarterly income statement shows the gross profit or loss generated by your business over a three-month period. It can also be referred to as a profit or loss account and is a crucial financial statement that shows the business’s operating income and expenditures, detailing your net income or net profits. An income statement is a financial report detailing a company’s income and expenses over a reporting period.
There are two ways of preparing P&L single step and multi step income statement. Single step gives you the revenue, expenses and the profit or loss of the business while Multi step breaks down operating revenues and operating expenses versus non-operating revenues and non-operating expenses. In a traditional income statement, expenses are deducted from revenues to derive net income, providing a comprehensive view of the company’s financial performance. On the other hand, a Contribution Margin Income Statement focuses on separating variable and fixed costs, revealing the contribution margin and its impact on profitability. It typically follows a specific structure, starting with the company’s sales or revenue, then deducting the cost of goods sold to calculate gross profit.
Income statements should be generated quarterly and annually to provide visibility throughout the year. Income statement evaluates the profit or loss of a business over a period of time, whereas balance sheets show the financial position of a business at a specific point in time. The other two important financial statements are the balance sheet and cash flow statement.
