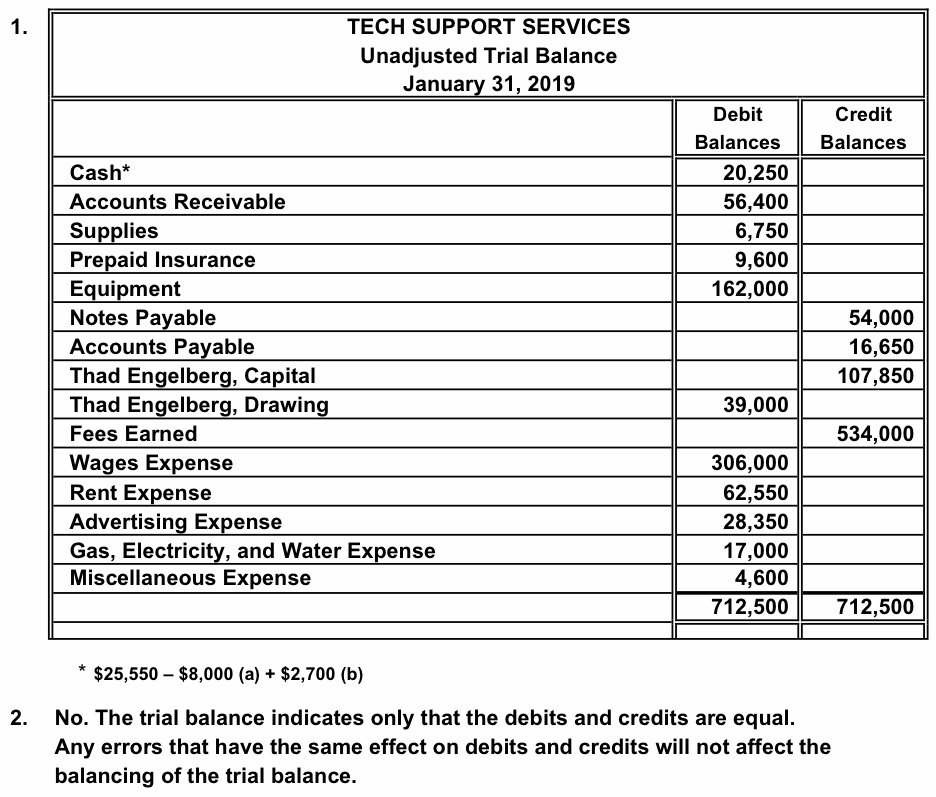
The purpose of the trial balance is to test the equality between total debits and total credits after the posting process. This trial balance is called an unadjusted trial balance (since adjustments are not yet included). Once all ledger accounts and their balances are recorded, the debit and credit columns on the trial balance are totaled to see if the figures in each column match each other. The final total in the debit column must be the same dollar amount that is determined in the final credit column.
Trial Balance vs. Balance Sheet
If they aren’t equal, the trial balance was prepared incorrectly or the journal entries weren’t transferred to the ledger accounts accurately. At the end of the accounting period, the accountant prepares a trial balance from the account information contained in the general ledger. This trial balance lists most of the assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses of the business, but these amounts are incomplete because adjusting entries have not yet been prepared. Preparation of unadjusted trial balance is the fourth step in the accounting cycle after identification of a transaction, recording it in journal and posting it in to ledger.
- Plus, the adjusted trial balance has one extra account mentioned, i.e., net/loss of income.
- By highlighting these mistakes, the trial balance acts as an accuracy check for a business, mitigating the risk of inaccuracies before you generate final financial statements.
- A trial balance is an accounting report you put together at the end of an accounting period to ensure the general accounting ledger is correct and the total debits match the total credits.
- A trial balance simply shows a list of the ledger accounts and their balances.
Can I Connect Wise to Shopify? Easy Integration Guide
A trial balance can be used to assess the financial position of a company between full annual audits. Companies can use a trial balance to keep track of their financial position, and so they may prepare several different types of trial balance throughout the financial year. A trial balance may contain all the major accounting items, including assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, expenses, gains, and losses. The key difference between a trial balance and a balance sheet is one of scope. A balance sheet records not only the closing balances of accounts within a company but also the assets, liabilities, and equity of the company. It is usually released to the public, rather than just being used internally, and requires the signature of an auditor to be regarded as trustworthy.
What are the three trial balances?
A trial balance is often used as a tool to keep track of a company’s finances throughout the year, whereas a balance sheet is a legal statement of the financial position of a company at the end of a financial year. Whereas, the adjusted trial balance (ATB) is the same as UTB except that it also includes any adjusting entries made during an accounting period. In the first and second closing entries, the balances of Service Revenue and the various expense accounts were actually transferred to Income Summary, which is a temporary account. The Income Summary account would have a credit balance of 1,060 (9,850 credit in the first entry and 8,790 debit in the second). You record all your accounting transactions and post them to the general ledger, then assess the debit and credit totals. It’s one of the first lines of defense against accounting errors and a pivotal report within double-entry bookkeeping.
What is your current financial priority?
What I mean by unadjusted balances is that none of the year-end balances have been adjusted by year-end adjusting journal entries yet. how to do bank reconciliation in xero numbers are simply the account balances from the general ledger. Given these definitions, the difference between the two types of trial balance are the adjusting entries made into the accounting system after the unadjusted trial balance is prepared. For instance, in our vehicle sale example the bookkeeper could have accidentally debited accounts receivable instead of cash when the vehicle was sold.
Each account with a balance in your accounting system, such as accounts receivable and accounts payable, appears in the trial balance with its respective balance–debits on the left and credits on the right. A trial balance is an internal report that itemizes the closing balance of each of your accounting accounts. It acts as an auditing tool, while a balance sheet is a formal financial statement.
He then took all the balances of each account in the Ledger and summarized them in an unadjusted trial balance which is as follows. The following unadjusted trial balance has been prepared from the ledger accounts of Company A. When the total debits and total credits are not equal, it is a clear indication that a mistake has been committed in the journalizing and/or posting process. There are no special conventions about how trial balances should be prepared, and they may be completed as often as a company needs them.
Companies initially record their business transactions in bookkeeping accounts within the general ledger. Depending on the kinds of business transactions that have occurred, accounts in the ledgers could have been debited or credited during a given accounting period before they are used in a trial balance worksheet. Furthermore, some accounts may have been used to record multiple business transactions. As a result, the ending balance of each ledger account as shown in the trial balance worksheet is the sum of all debits and credits that have been entered to that account based on all related business transactions. After the unadjusted trial balance is prepared and it appears error-free, a company might look at its financial statements to get an idea of the company’s position before adjustments are made to certain accounts. A more complete picture of company position develops after adjustments occur, and an adjusted trial balance has been prepared.
